While you don't have anything to worry about if you bought your computer from a big-box retailer or straight from a manufacturer like HP, you'll be faced with a potentially crucial decision if you're building (or custom-buying) a fire-breathing, benchmark-eating computer: Should you chill your PC with a traditional air cooling solution or a pricier, yet more efficient liquid-cooling system? That question has many aspects to consider before you can answer it.
Cooling methods explained
The secret to harnessing the cooling power of air lies in fans—lots of fans. Your typical air-cooled PC is packed with case fans, graphics card fans, and a CPU fan or two—positioned atop a big metal heat sink—to keep your expensive components nice and frosty.A water-cooling system, on the other hand, employs a series of coolant-filled tubes, a radiator, water blocks (the equivalent of heat sinks), and a couple of other components to keep your PC feeling refreshed. You'll even need a few fans to push around all the water! Our guide to setting up a liquid-cooled PC explains a basic (ha!) system in exacting detail.
Got it? Good. Defining air cooling and liquid cooling is the easy part. The trickier bit is making the decision to use one or the other.
Air cooling
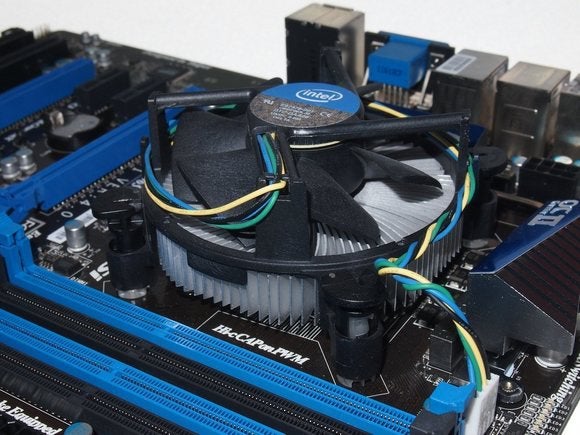

Graphics cards and computer processors pretty much always ship with powerful stock fans—you know, the ones that sound like a plane taking off when they roar into action. Those, combined with case fans, make up the Holy Trifecta of air cooling within a typical desktop PC.
 Noctua
NoctuaAlso consider the cost to your sanity. It’s a lot easier to use four screws to attach a fan to your case than it is to build your own water cooling setup.
Traditional air cooling has three major downsides, though. First, fans aren't as efficient as water cooling, which can pose a problem with severely overclocked processors or in particularly beefy rigs filled with multiple graphics cards. Second, the heat sinks on powerful CPU coolers can get big. Finally, fans are loud.
Water cooling pros
The act of switching from air to liquid cooling represents a personal milestone in one’s computer-building life. You, young PC Padawan, are now a desktop Jedi.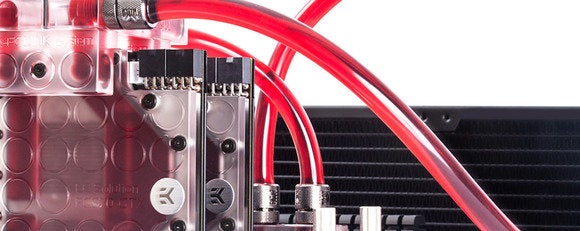 EKWaterblocks
EKWaterblocksEven if you don't tax your rig enough to need a bigger cooling boost, a cheap self-contained water cooling loop—more on those later—can help lower your PC's sound output. Water cooling is much quieter than stuffing your case full of fans.
There's also the issue of space. A huge heat-sink/fan combination might perform well enough, but the best CPU coolers eat up a ton of real estate inside your case. Liquid cooling requires much less space, and it looks a lot niftier to boot. You can't discount the cool factor of a case full of colorful, liquid-filled tubes!
Water cooling cons
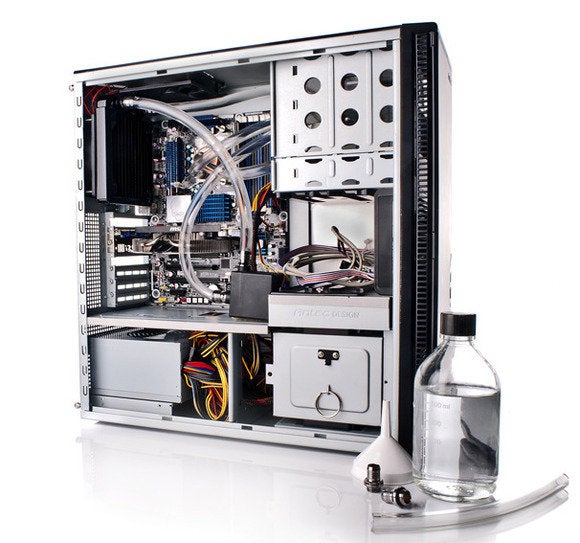

Quality matters in a liquid-cooling setup: You don’t want to buy cheap parts to save a few bucks and end up dousing your pricey PC components in brightly hued coolant.
The homework involved is another drawback. Generating the parts list is going to take a little planning if you're not buying a prepackaged kit. You’ll have to pick up a water block for your CPU that fits its socket, fittings that match your block and tubing size, the tubing itself, a pump, a reservoir, a radiator, a fan (or fans) for the radiator, and the coolant itself. And that’s just a typical setup for the most bare-bones configuration you can build. If you want to power separate loops for your video card, motherboard, RAM, or hard drives, you’ll have to do even more planning and purchasing.

Then there’s the installation itself. Simply put, your first adventures in water-cooling land could very well be fraught with peril. Installing loops isn’t exactly newbie-friendly, and the process might be more involved than you’re comfortable with, even if you’ve installed a typical fan-based aftermarket CPU cooler or two.
Which reminds me: Connecting your tubing and fittings in a secure and safe fashion is going to be your number-one issue when building your first water-cooling setup. You will spring a leak in some fashion. You'll want to construct and test your liquid-cooling system outside of your PC to ensure its fortitude before installing it around your expensive electronics. Component manufacturers aren't likely to replace flooded electronics, and the manufacturers of your water cooling parts certainly aren’t going to foot the bill.
Self-contained liquid coolers

Self-contained or "sealed" liquid-cooling kits—preassembled and completely sealed, they start at around just $60—allow you reap the benefits of a simple water-cooling setup without having to deal with any of the messy particulars. You just need to attach a water block to your CPU and a radiator/fan combination to your case, and you’re off to the races, with nary a drop of coolant to worry about. You may lose customization options if you use self-contained kits like Corsair’s Hydro H-series or NZXT's Kraken-series coolers, but you also lose most of the headaches typically associated with do-it-yourself liquid cooling. Leakage is highly unlikely as long as you don't bend or twist the tubing at sharp, weird angles.
Installing a self-contained liquid-cooling kit is about on a par with the difficulty of installing an aftermarket cooler for your CPU. If you need to water-cool only your overclocked processor, a sealed liquid cooler is a compelling option. Stick to DIY loops if you want to liquid-cool more than the single component, however—or if you want the bling factor of clear tubes filled with colorful coolant. Most sealed coolers are opaque.
Conclusion
So, which is better? Air cooling or water cooling? The answer depends on your particular usage needs.One size does not fit all when it comes to case cooling, but most people can get by with fans alone. It's easy, and it's cheap. If, on the other hand, you’re an enthusiast who needs the best cooling possible for your flaming CPU and a gaggle of graphics cards, a DIY water-cooling setup is in your future. Finally, try a sealed liquid cooler if you're considering liquid cooling either to keep your overclocked processor chilled or simply to benefit from reduced system noise.
Sign up here with your email

ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon